Men with type 2 diabetes have a higher risk of erectile dysfunction than other men and are less responsive to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor (PDE5i) drugs, which are the first-line therapy for this condition.
It’s not surprising that PDE5i efficacy is impacted in men with diabetes. These drugs block degradation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) after its activation by nitric oxide, thus maintaining the vascular smooth muscle relaxation responsible for erection.
Hyperglycemia can decrease bioavailability of nitric oxide and impair vascular smooth muscle responsiveness, thereby compromising erectile function and limiting the effectiveness of PDE5 inhibitors.
In a group of 1574 men presenting with sexual dysfunction, Boeri and colleagues assessed erectile function using the International Index of Erectile Dysfunction at the beginning of the study and after using a PDE5 inhibitor for three months.
These measures were related to self-reported previous diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, or glycaemic control (based on fasting plasma glucose concentrations, glucose tolerance and HbA1C levels) to classify men as normoglycaemic or prediabetic.
Analysis was restricted to 446 men who satisfied strict inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Erectile function was poorer in men with diabetes than in men with normal glycaemic control, consistent with previous studies, and was intermediate in men with prediabetes.
Improvements in erectile dysfunction occurred in response to PDE5 inhibitor use in all groups, but the treatment was more effective in men with normoglycaemia than men with diabetes and was intermediate for men with prediabetes.
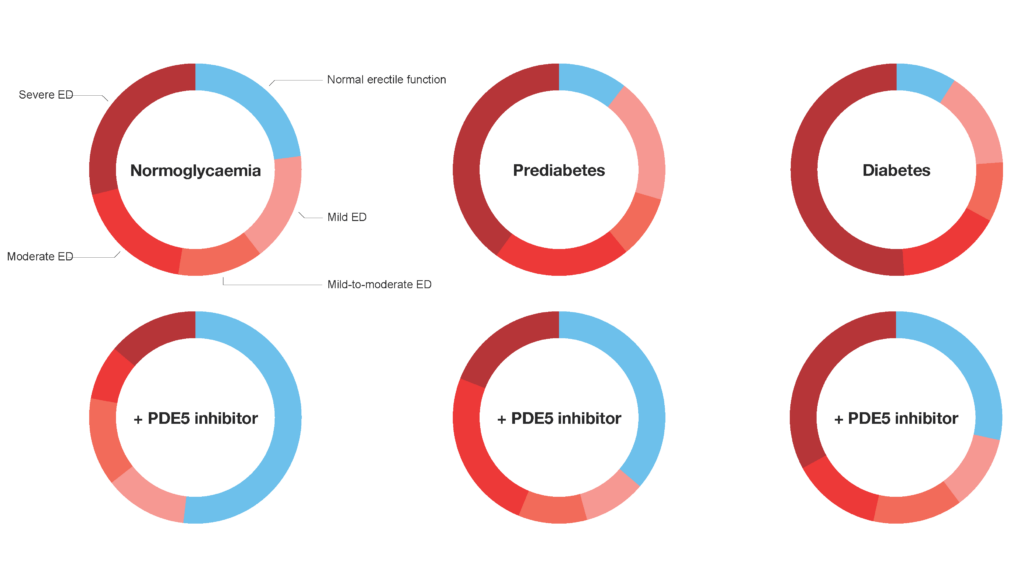
The fact that PDE5 inhibitors work in men with prediabetes and diabetes, but not as well as in men with normal glycaemic control, has important implications for clinical care.
Examination of glycaemic control in all men presenting with erectile dysfunction offers an opportunity to identify men with prediabetes. This will allow interventions to correct poor glycaemic control and prevent progression to diabetes for some men.
The knowledge that poor glycemic control affects not only a man’s erectile function but also his response to treatment might just be enough to motivate action.
Summary
Even moderate impairment of a man’s glycaemic control is enough to affect his erectile function and his response to PDH5 inhibition.














