Testicular volume
Testicular volume is assessed using an orchidometer; a sequential series of beads ranging in size from 1 mL to 35 mL (see Image 1).
Normal testicular volume ranges
| Childhood | Puberty | Adulthood |
|---|---|---|
| < 3ml | 4-14ml | 15-35ml |
Examination of secondary sexual characteristics
Penile Growth

Image 1 – Orchidometer
Why use an Orchidometer?
Testicular volume is important in the assessment of normal development and diagnosis of androgen deficiency, infertility and Klinefelter syndrome.
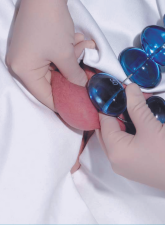
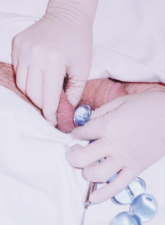
Image 2 – 30mL (normal)(left)/4mL (Klinefelter syndrome)(right)
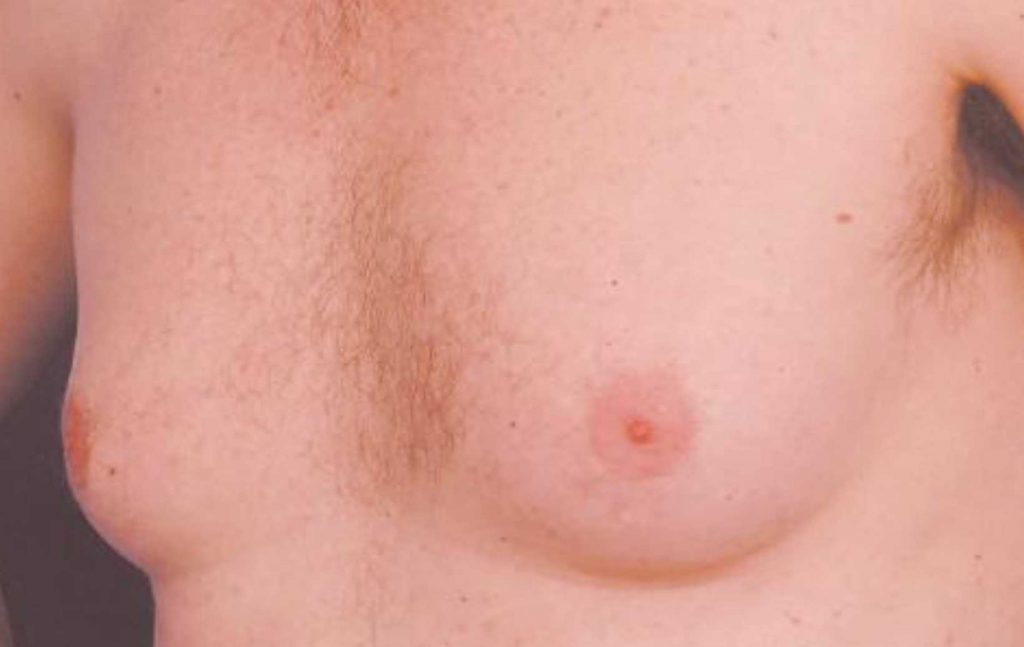
Image 3 – Gynecomastia
(Photo courtesy of Mr G Southwick, Melbourne Institute of Plastic Surgery)
Examination of testis and scrotal contents
| Testis | Gently palpate the testis between your thumb and first two fingers. Note: Atrophic testes are often more tender to palpation than normal testes. | If a testis cannot be felt, gently palpate the inguinal canal to see if testis can be ‘milked’ down. Note: Testis retraction can be caused by cold room temperature, anxiety and cremasteric reflex. | Examine the testis surface for irregularities. It should be smooth, with a firm, soft rubbery consistency. Note: A tumour may be indicated by deep or surface irregularity, or differences in consistency between testes. |
| Epididymis | Locate the epididymis, which lies along the posterior wall of the testis. It should be soft, slightly irregular and non-tender to touch. | Tenderness, enlargement or hardening can occur as a result of obstruction (vasectomy) or infection. This can be associated with obstructive infertility. Cysts in the epididymis are quite common. These are something mistaken for a testicular tumour. | |
| Vas deferens | Locate the vas deferens, a firm rubbery tube approximately 2-3 mm in diameter. | Nodules/thickening around the vas deferens ends may be apparent after vasectomy. | |
| The vas deferens should be distinguished from the blood vessels and nerves of the spermatic cord. | Absence of the vas deferens is a congenital condition associated with low semen volume and azoospermia. | ||
| Varicocele | Perform examination with the man standing. A Valsalva manoeuvre or coughing helps delineate smaller varicoceles. | Indicators include: – Palpable swelling of the spermatic veins above testis – Swelling is usually easy to feel and can be compressed without discomfort – Nearly always on left side – Associated with infertility. | See image below. |
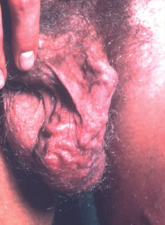
Examination of penile abnormalities
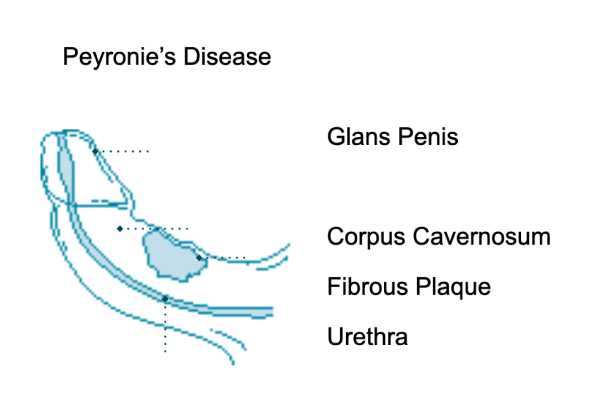
| Peyronie’s disease | Fibrous tissue, causing pain and curvature of the erect penis. Check for tenderness or thickening. |
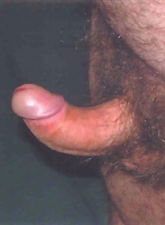
| Phimosis | The foreskin cannot be pulled back behind the glans penis. Can be normal in boys up to 5-6 years. |
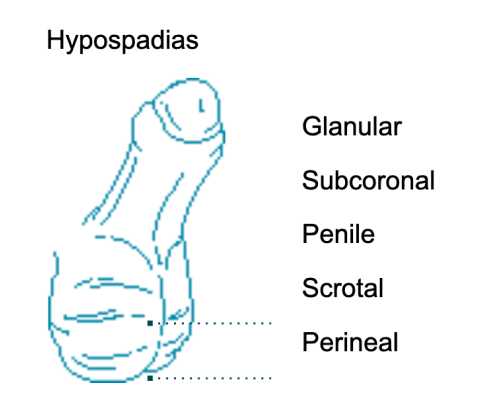
| Hypospadias | Abnormal position of meatus on the underside of the penile shaft. May be associated with a notched penile head. |
| Urethral stricture | Abnormal urethral narrowing, which alters urination. Can be caused by scar tissue, disease or injury. |
| Micropenis | May indicate androgen deficiency prior to puberty. Rare. |
Clinical review
Clinical review by Dr Darren Katz, Men’s Health Melbourne









